Note
Click here to download the full example code
Fixing common date annoyances¶
Matplotlib allows you to natively plots python datetime instances, and for the most part does a good job picking tick locations and string formats. There are a couple of things it does not handle so gracefully, and here are some tricks to help you work around them. We'll load up some sample date data which contains datetime.date objects in a numpy record array:
In [63]: datafile = cbook.get_sample_data('goog.npz')
In [64]: r = np.load(datafile)['price_data'].view(np.recarray)
In [65]: r.dtype
Out[65]: dtype([('date', '<M8[D]'), ('', '|V4'), ('open', '<f8'),
('high', '<f8'), ('low', '<f8'), ('close', '<f8'),
('volume', '<i8'), ('adj_close', '<f8')])
In [66]: r.date
Out[66]:
array(['2004-08-19', '2004-08-20', '2004-08-23', ..., '2008-10-10',
'2008-10-13', '2008-10-14'], dtype='datetime64[D]')
The dtype of the NumPy record array for the field date is datetime64[D]
which means it is a 64-bit numpy.datetime64 in 'day' units.
If you plot the data,
you will see that the x tick labels are all squashed together.
import matplotlib.cbook as cbook
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
r = (cbook.get_sample_data('goog.npz', np_load=True)['price_data']
.view(np.recarray))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(r.date, r.close)
ax.set_title('Default date handling can cause overlapping labels')
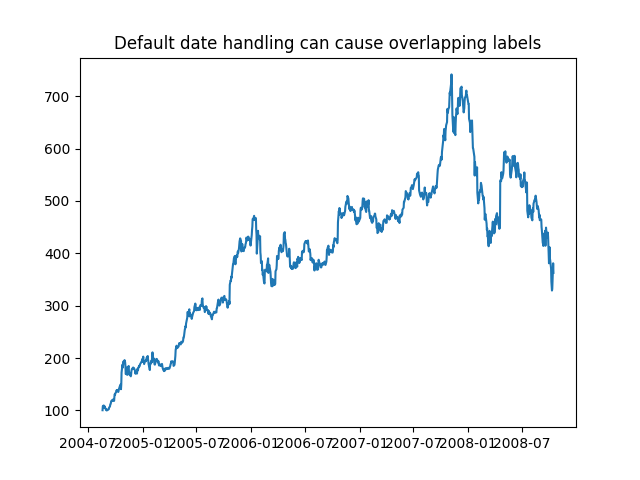
Out:
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Default date handling can cause overlapping labels')
Another annoyance is that if you hover the mouse over the window and look in the lower right corner of the Matplotlib toolbar (Default UI) at the x and y coordinates, you see that the x locations are formatted the same way the tick labels are, e.g., "Dec 2004".
What we'd like is for the location in the toolbar to have a higher degree of
precision, e.g., giving us the exact date out mouse is hovering over. To fix
the first problem, we can use Figure.autofmt_xdate and to fix the second
problem we can use the ax.fmt_xdata attribute which can be set to any
function that takes a scalar and returns a string. Matplotlib has a number
of date formatters built in, so we'll use one of those.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(r.date, r.close)
# Rotate and align the tick labels so they look better.
fig.autofmt_xdate()
# Use a more precise date string for the x axis locations in the toolbar.
ax.fmt_xdata = mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d')
ax.set_title('fig.autofmt_xdate fixes the labels')
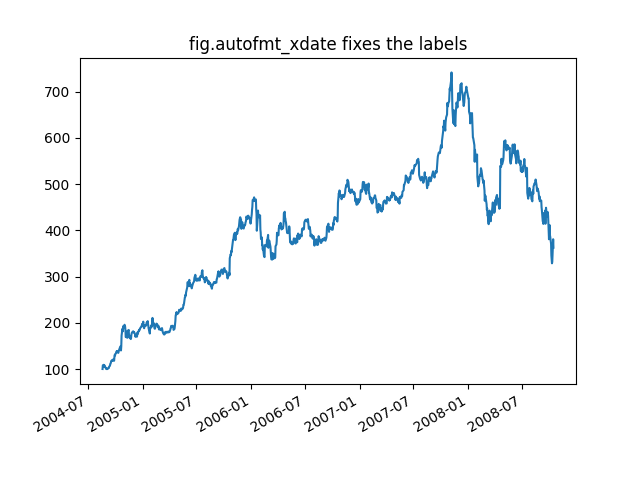
Out:
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'fig.autofmt_xdate fixes the labels')
Now when you hover your mouse over the plotted data, you'll see date format strings like 2004-12-01 in the toolbar.
plt.show()
Keywords: matplotlib code example, codex, python plot, pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery