Note
Click here to download the full example code
Placing text boxes¶
When decorating axes with text boxes, two useful tricks are to place the text
in axes coordinates (see Transformations Tutorial),
so the text doesn't move around with changes in x or y limits. You
can also use the bbox property of text to surround the text with a
Patch instance -- the bbox keyword argument takes a
dictionary with keys that are Patch properties.
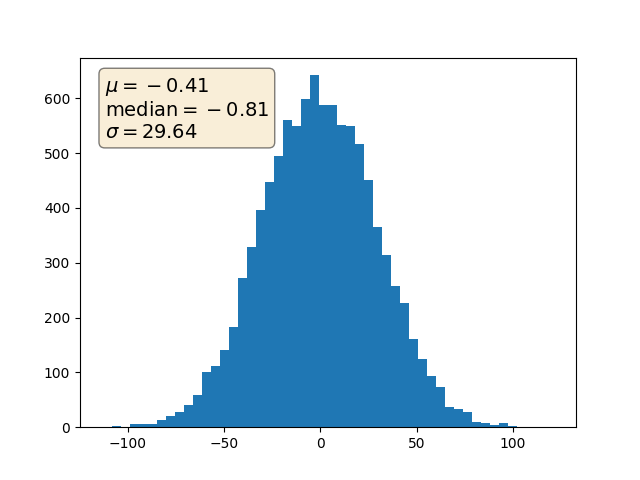
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(19680801)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = 30*np.random.randn(10000)
mu = x.mean()
median = np.median(x)
sigma = x.std()
textstr = '\n'.join((
r'$\mu=%.2f$' % (mu, ),
r'$\mathrm{median}=%.2f$' % (median, ),
r'$\sigma=%.2f$' % (sigma, )))
ax.hist(x, 50)
# these are matplotlib.patch.Patch properties
props = dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='wheat', alpha=0.5)
# place a text box in upper left in axes coords
ax.text(0.05, 0.95, textstr, transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=14,
verticalalignment='top', bbox=props)
plt.show()
Keywords: matplotlib code example, codex, python plot, pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery